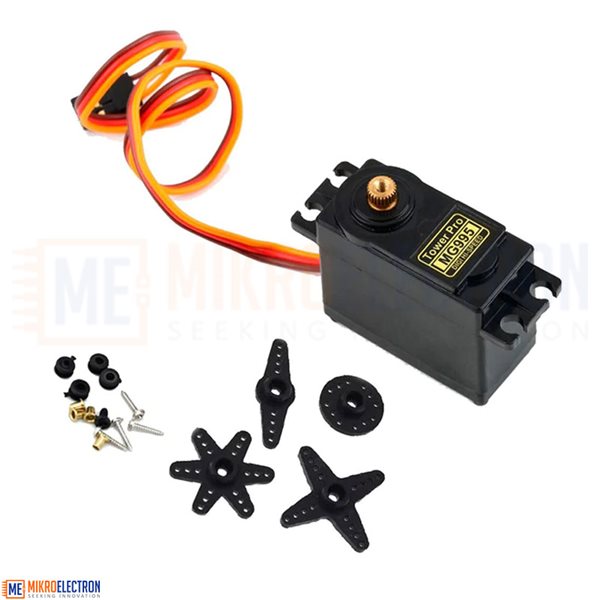
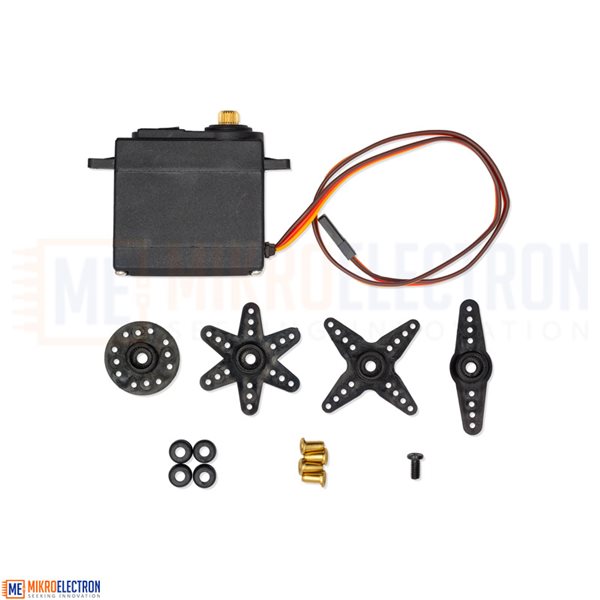
180 degree servo MG995 Motor High Quality
Description:
The Servo Motor MG995 is a standard size servo with a range of 180 degrees with good torque and moderate speed.
KEY FEATURES OF SERVO MOTOR MG995:
- Standard (medium) size servo
- High torque of up to 12kg/cm
- 180 degree rotation
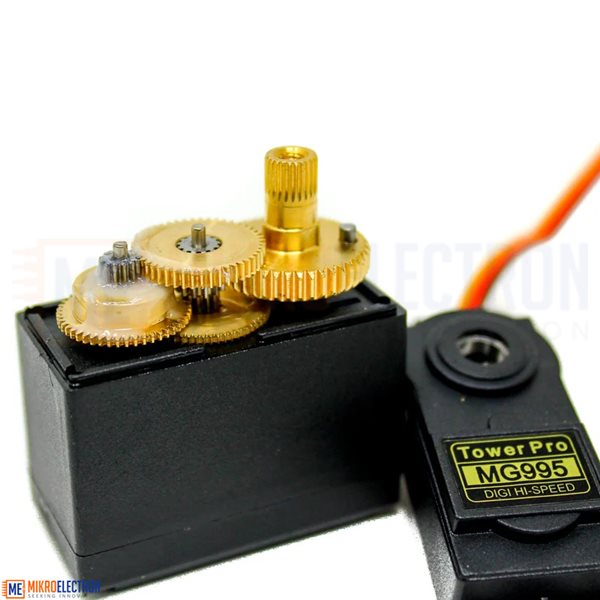
- Metal (Brass & aluminum) gears
- Analog drive
These servos have good torque for the cost and work well for experimenting with robotic arms, steering controls and other applications that require a fair amount of grunt.
The high torque capability comes at the expense of fast speed of movement due to the gearing. A 60° rotation takes about 0.2 seconds. That is fine for robotic arm movement or slower speed crawler steering for instance, but too slow for a fast moving RC car or flight controls.
Servo motors can be commanded to go to a specific position and so are the usual go-to motor when accurate positioning is needed, such as for turning the front wheels on an RC model for steering or pivoting a sensor to look around on a robotic vehicle.
Servo motors are comprised of a DC motor, gears, a potentiometer to determine its position and a small electronic control board.
Servos usually have a specified limited range. This is usually specified as 180 degrees. Frequently the actual range is not quite the full 180 degrees and is limited by the mechanical gears and potentiometer used for position sensing that is contained in the device. If the motor is run all the way to 0 or 180, it may start making unhappy sounds and start vibrating as it tries to drive to a position that it cannot get to. This causes a high stall current condition and has the potential of stripping gears and eventually burning out the drive electronics or damaging the motor, so it is best to either drive it to a safely reduced range such as 20-160 or experiment a bit to determine the actual usable range if you want to maximize the range.
Some versions of the servo may be specified as 360 degree continuous rotation. In this case, the servo mechanical stops and potentiometer have been removed or disconnected and is designed to rotate continuously in either direction and is primarily used for drive wheels.
Servos expect to see a pulse on their PWM pin every 20mSec (50Hz). The pulse is active HIGH and the width of the pulse determines the position (angle) of the servos shaft. The pulse can vary between 1mSec and 2mSec. A 1mSec pulse positions the shaft at 0 degrees. A 1.5mSec pulse positions the shaft at 90 degrees (centered in its range). A 2mSec pulse positions the shaft at 180 degrees. Pulses with values between these can be used to position the shaft arbitrarily.
Features:
|
Motor Model |
Generic MG995 (China) |
|
|
Drive Type |
Analog |
|
|
Degree Rotation |
180° (±10°) |
|
|
Operating Ratings |
||
|
Voltage |
4.8-6VDC (5V Typical) |
|
|
Current (idle) |
10mA (typical) |
|
|
Current (typical during movement) |
170-400mA |
|
|
Current (stall) |
1.3 – 1.5A (measured) |
|
|
Stall Torque |
12kg-cm (typical) |
|
|
Speed |
0.2s / 60 degree (varies with VDC) |
|
|
Dimensions |
||
|
Cable Length |
28cm (11″) |
|
|
Motor Housing L x W x H |
40.9 x 20 x 39mm (1.6 x 0 .79 x 1.53″) |
|
|
Motor Height (w/ shaft) |
45mm (1.77″) |
|
|
Motor Housing Width with Mounting Ears |
54mm (2.13″ |
|
Kit include:
1 x 180 degree servo MG995 Motor High Quality
Mikroelectron Code:
/*
Exercise Servo motor
Use a potentiometer on pin A0 to command a servo attached to pin 9 to move to
a specific position. The Servo MIN_VALUE and MAX_VALUE can be adjusted to
avoid hitting the servo stops
Uses built-in Servo.h library
*/
#include "Servo.h"
#define SERVO_PIN 9 // Can use any PWM pin
#define POT_PIN A0 // Can use any analog pin
#define MIN_VALUE 3 // Minimum Servo position
#define MAX_VALUE 180 // Maximum Servo position
#define AVGNUM 25 // Number of interations to average readings over
Servo servo; // creates servo object used to control the servo motor
int value_pot = 0; // Current value of the potentiometer
int value_servo = 0; // Current servo position
int value_servo_old = 0; // Used to hold old servo value to look for change.
int avg_value = 0;
//===============================================================================
// Initialization
//===============================================================================
void setup()
{
servo.attach(SERVO_PIN); // assigns PWM pin to the servo object
Serial.begin (9600); // Set Serial Monitor window comm speed
}
//===============================================================================
// Main
//===============================================================================
void loop()
{ // Average some readings to help filter out A/D noise to minimize servo hunting
for(int i=0; i<AVGNUM; ++i) {
value_pot = analogRead(POT_PIN); // Reads value of the pot (0 to 1023)
avg_value += value_pot;
delay(1);
}
avg_value /= AVGNUM;
value_servo = map(avg_value, 0, 1023, MIN_VALUE, MAX_VALUE); // remap pot to servo value
value_servo = constrain(value_servo, MIN_VALUE, MAX_VALUE); // constrain within bounds
if (value_servo != value_servo_old) { // If change, update servo position
servo.write(value_servo); // Send new position to servo
Serial.print("Pot Value: "); // Update Serial Monitor window with what's going on
Serial.print(avg_value);
Serial.print(" Servo Value: ");
Serial.println(value_servo);
value_servo_old = value_servo;
}
}
Related Products
subscribe to our weekly newsletter